SQL Joins - The Coding Shala
Home >> Learn SQL >> SQL JOINS
Table 2. 'dept' table -
The following SQL query will select the records where dept_no is same on both the tables -
SQL Joins
The SQL Join Clause is used to combine records from two or more tables based on some common columns.
Example
Table 1. 'emp' table -
emp_id emp_name city dept_no salary 1 Akshay Pune 101 50000 3 Nikhil Pune 101 51000 5 Mohit Delhi 103 40000 6 Shubham Surat 105 42000 7 Akash Mumbai 106 45000
Table 2. 'dept' table -
dept_no dept_name total_emp 101 Product Dev 50 102 Consulting 100 103 Product Consult 20 104 Marketing 150 105 Sales 250
The following SQL query will select the records where dept_no is same on both the tables -
SQL >> select emp.emp_id, emp.emp_name, emp.salary, emp.dept_no, dept.dept_name from emp, dept where emp.dept_no = dept.dept_no; Output >> emp_id emp_name salary dept_no dept_name 1 Akshay 50000 101 Product Dev 3 Nikhil 51000 101 Product Dev 5 Mohit 40000 103 Product Consult 6 Shubham 42000 105 Sales
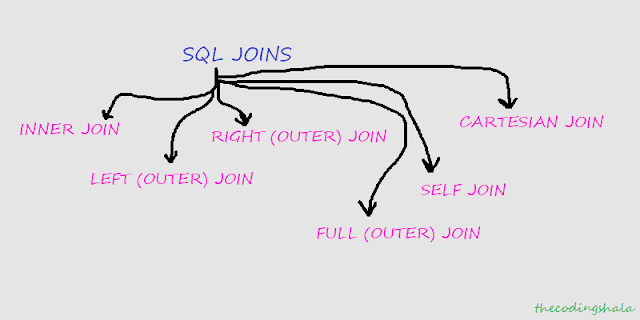
Types of SQL JOINs
Following are the different types of Joins in SQL -
- INNER JOIN - Return records that have matching values in both the tables.
- LEFT (OUTER) JOIN - Return all the rows from the left table, even if there are no matches in the right table.
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN - Return all the rows from the right table, even if there are no matches in the left table.
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN - Return all the rows when there is a match either on the left or right table.
- SELF JOIN - is used to join a table to itself.
- CARTESIAN JOIN - Return the cartesian product of the sets of rows from the joined tables.
Other Posts You May Like


Comments
Post a Comment