Java Runtime Polymorphism - The Coding Shala
Home >> Learn Java >> Java Runtime Polymorphism
Java Runtime Polymorphism
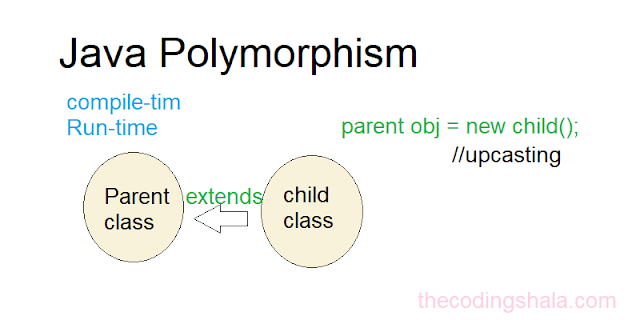
Polymorphism means many forms. There are two types of polymorphism in Java:
- compile-time polymorphism
- Runtime polymorphism
Runtime polymorphism is also known as Dynamic Method Dispatch. Runtime polymorphism is a process in which a call to an overridden method is resolved at runtime, not at the compile-time.
An overridden method is called through the reference variable of a superclass. We use upcasting for runtime polymorphism.
Upcasting
If the reference variable of Parent class refers to the object of Child class, it is known as upcasting.
The following code shows how to achieved runtime polymorphism using upcasting.
class Parent{} class Child extends Parent{} Parent p = new Child();//upcasting
Example of Java Runtime Polymorphism
This following example explains java runtime polymorphism:
//Runtime polymorphism example //thecodingshala.com class Parent{ void Display(){ System.out.println("Inside Parent class"); } } class Child extends Parent{ void Display(){ System.out.println("Inside Child class"); } } class GrandChild extends Child{ void Display(){ System.out.println("Inside GrandChild class"); } } class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Parent p1 = new Parent(); p1.Display(); Parent p2 = new Child(); //upcasting p2.Display(); //override Parent p3 = new GrandChild(); p3.Display(); //works on multilevel inhertance also } }
Output:
Inside Parent class Inside Child class Inside GrandChild class
Java Runtime Polymorphism with Data Member
In Java, we can override a method but not the data members so runtime polymorphism can not be achieved by data members. The following example explains it:
///runtime polymorphism with data member //thecodingshala class Parent{ int num = 10; } class Child extends Parent{ int num = 30; } class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Parent p = new Child(); System.out.println(p.num); }}
Output:
10
Other Posts You May Like


Comments
Post a Comment