Merge Sort Algorithm - The Coding Shala
Last Updated: 20-Jan-2021
Home >> Algorithms >> Merge Sort Algorithm
In this post, we will learn what is Merge Sort Algorithm and how it works. We will write a Java Program for Merge Sort.
Merge Sort Algorithm
Merge Sort is an efficient and general-purpose sorting algorithm. It is a classic example of the divide-and-conquer algorithm.
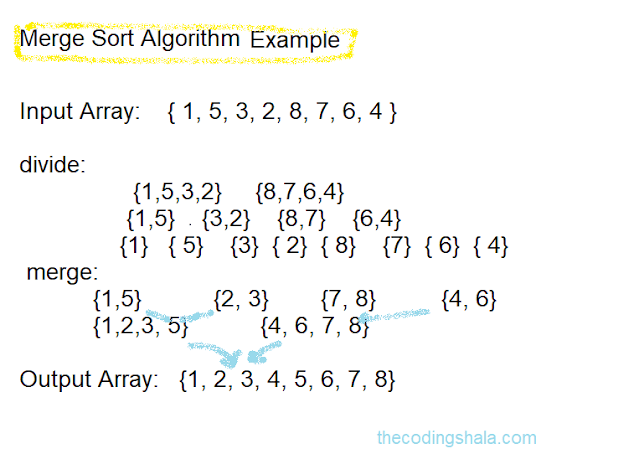
The merge sort algorithm can be divided into three steps, like all the divide-and-conquer algorithm:
step 1. Divide the given unsorted list into several sublists. (Divide)
step 2. Sort each of the sublists recursively. (Conquer)
Step 3. Merge the sorted sublists to produce a new sorted list. (Combine)
Here is an example that explains the working of the merge sort algorithm:
The time complexity of Merge Sort Algorithm
The time complexity of the merge sort algorithm is O(NlogN), where N is the length of the input list.
Merge Sort Algorithm Java Program
Java Program:
import java.util.Arrays; //merger sort //the coding shala class Main{ public static int[] merge_sort(int[] input) { int len = input.length; if(len<=1) return input; int mid = len/2; //divide into left and right array by mid int[] left = merge_sort(Arrays.copyOfRange(input, 0, mid)); int[] right = merge_sort(Arrays.copyOfRange(input, mid, len)); //merge both arrays return merge(left, right); } public static int[] merge(int[] left, int[] right) { int len_left = left.length; int len_right = right.length; int[] result = new int[len_left+len_right]; int left_index = 0, right_index = 0, result_index = 0; //combine the arrays in order while(left_index < len_left && right_index < len_right) { if(left[left_index] < right[right_index]) { result[result_index] = left[left_index]; result_index++; left_index++; }else { result[result_index] = right[right_index]; result_index++; right_index++; } } //if left array elements remains while(left_index < len_left) { result[result_index] = left[left_index]; result_index++; left_index++; } //if right array element remains while(right_index < len_right) { result[result_index] = right[right_index]; result_index++; right_index++; } return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] input = {1,5,3,2,8,7,6,4}; input = merge_sort(input); for(int i=0;i<input.length;i++) { System.out.print(input[i]+" "); } } }
- Insertion Sort Algorithm
- Counting Sort Algorithm
- Bucket Sort Algorithm
- Bubble Sort Algorithm
- Binary Search Algorithm


Comments
Post a Comment